Early detection saves lives.
Let’s start with yours.
To get started, ask to talk to a HALO Patient Navigator at your imaging center.
Know More. Act Sooner.
HALO’s Genetic and Breast Pathways help detect risk for inherited cancer predispositions and provide personalized insights - so you can take control of your health early. Ask for your Patient Navigator at your center offering Halo Pathways.
Genetic Testing Gave Me Clarity, Confidence, and Control
Kavita, HALO Patient and employee
Kavita’s story
“Knowing my results was the better option, rather than living in doubt. Genetic testing gave me peace of mind and the power to make informed decisions—not just for myself, but for my future family.”
When cancer is caught sooner,
treatment success is higher.
1 in 8 women
will be diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime¹
1 in 6 people
meet genetic testing criteria, but only a small fraction have had genetic testing²
1 in 9 men
will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime³
will be diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime.
meet genetic testing criteria, but only a small faction have had genetic testing.
will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime.
for both men and women is cardiovascular disease
Is Inherited Cancer Risk a Factor for You?
The average person has up to a 40% chance of developing cancer during their lifetime.⁴
However, your family history may increase your personal risk—so it’s important to start by reviewing it carefully.
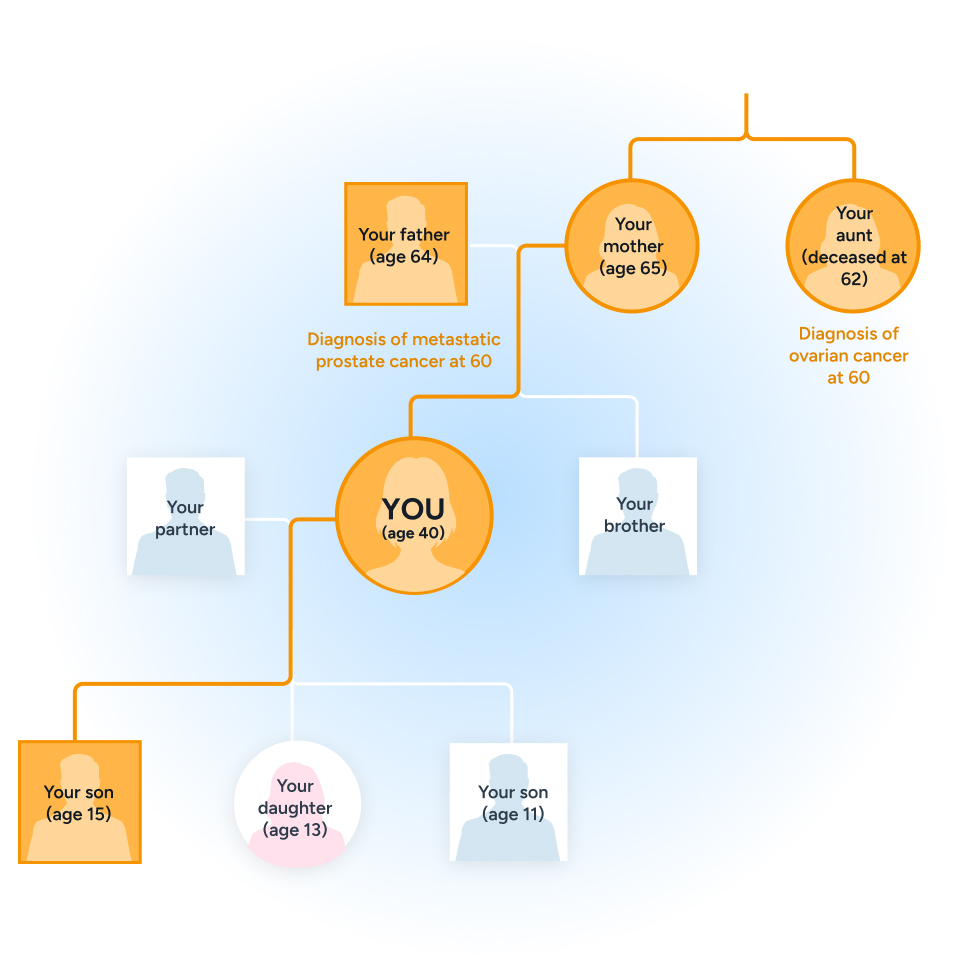
Do close relatives (parents, siblings, children, grandparents, aunts, uncles, nieces, nephews) have a history of cancer? Specifically, breast, ovarian, prostate, pancreatic, colon, endometrial (uterine, not cervical), or stomach (gastric) cancer?
Anyone diagnosed before age 50?
Did any close relative have more than one cancer?
Is there a history of rare types of cancer in the family, such as male breast cancer, pancreatic or ovarian cancer?

Meet Mary
How HALO helped a patient get their health back on track
Mary’s father’s mother passed away from breast cancer at 45. After turning 35, her doctor recommended a mammogram. Mary also had the HALO Genetic Health PathWay™ cancer genetic test.
What does this mean for Mary?
Mary tested positive for a BRCA2 variant, which increases the risk of breast and other cancers.⁵ Her HALO Nurse Practitioner recommended a screening breast MRI, in line with established standard of care. While Mary’s mammogram was normal, the MRI detected breast cancer early, leading to successful treatment.
How does this impact Mary’s family?
Mary shared her results with her family so they, too, could take action for personalized screening and prevention. Her siblings and children each had a 50% chance of carrying the same variant. In line with standard of care, her family was recommended to consider genetic testing.
How much does testing cost?
Most commercial and federally funded insurance plans cover cancer predisposition testing, and the majority of patients have no out of pocket costs, when certain criteria are met. For those who do have out-of-pocket expenses, we offer options to make testing accessible and affordable.
Early detection saves lives. Let’s start with yours.
Ask for your Patient Navigator at your center offering Halo Pathways.
Understanding Your Risk:
BRCA2 and Cancer Screening
A single gene variant can increase the risk for several different types of cancer. HALO Precision Diagnostics focuses on genes that have consensus screening guidelines established – so the results can lead to clear, actionable next steps. The table below summarizes cancer risks associated with BRCA2 variants.
| Cancer | Lifetime Risk | Screening highlights from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network* |
|---|---|---|
| 45–69% | Annual breast MRI beginning at age 25, add mammogram at 30 | |
| 11–17% | Limitations of available screening Speak with your healthcare provider to discuss risk reducing options | |
| 6–7% | Annual breast exam from 35; consider annual mammogram starting at age 50, or earlier depending on family history | |
| 20–30% | Consider baseline PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen) beginning at age 40; with follow-up dependent on results | |
| 2–5% | Screening can be considered, if there is close relative who was diagnosed; age to start depends on age at diagnosis of relative | |
| Possibly increased | Consider yearly skin checks |
* to be reviewed in detail with your healthcare providers if a BRCA2 variant is identified
Breast cancer (Women)
Lifetime Risk
- 45–69%
Screening highlights from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network*
- Annual breast MRI beginning at age 25, add mammogram at 30
Ovarian cancer
Lifetime Risk
- 11–17%
Screening highlights from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network*
- Limitations of available screening
- Speak with your healthcare provider to discuss risk reducing options
Male Breast cancer
Lifetime Risk
- 6–7%
Screening highlights from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network*
- Annual breast exam from 35; consider annual mammogram starting at age 50, or earlier depending on family history
Prostate cancer
Lifetime Risk
- 20–30%
Screening highlights from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network*
- Consider baseline PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen) beginning at age 40; with follow-up dependent on results
Pancreatic cancer
Lifetime Risk
- 2–5%
Screening highlights from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network*
- Screening can be considered, if there is close relative who was diagnosed; age to start depends on age at diagnosis of relative
Melanoma
Lifetime Risk
- Possibly increased
Screening highlights from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network*
- Consider yearly skin checks
*to be reviewed in detail with your healthcare providers if a BRCA2 variant is identified
Kavita’s story
Genetic Testing Gave Me Clarity, Confidence, and Control
Knowing my results was the better option, rather than living in doubt. Genetic testing gave me peace of mind and the power to make informed decisions – not just for myself, but for my future family.
How does it work?
Step 1: saliva sample
At your appointment, your DNA is collected through a saliva sample.
Step 2: gene analysis
The sample is analyzed for genetic variations associated with inherited cancer risks.
Step 3: results
In approximately 21-30 days, you will receive a detailed report to review with your healthcare provider. Please note, insurance processing can impact result turnaround.
Frequently asked questions
It will depend on what type of testing you had previously. There have been significant updates to genetic testing in the last 10 years. If you were tested prior to 2015, it may be time to consider testing again.
If you had previous testing as part of ancestry testing or for general health screening, your testing may not have included full analysis of the genes associated with an inherited cancer predisposition. If this was testing you purchased directly, rather than ordered through a healthcare professional, additional testing may be indicated.
If your family history has changed significantly since you had your original testing, it may be important to review your family history to determine if additional testing is indicated.
Your genetic test results are private. Only you will get the results, and it’s up to you if you want to share them with your doctor or anyone else helping with your care.
Yes. There is a federal law called GINA—the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act. GINA protects you by making it illegal for health insurance companies to raise your rates, deny coverage, or drop you because of your genetic test results. It also means your employer can’t fire you, refuse to hire you, or treat you differently at work because of your genetic test results.
GINA has limitations. This law alone doesn’t cover life insurance, long-term care, or disability insurance. Some states have enacted their own laws that provide additional coverage.
Laser Focal Therapy (LFT) Prostate Cancer Surgery
We use Laser Focal Therapy (focal laser ablation) for the treatment of low-to-intermediate prostate cancer. This prostate laser surgery can also be used to help improve the symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Laser Focal Therapy has demonstrated hugely successful results⁶:
- 1% erectile dysfunction compared to about 50% with whole gland prostatectomy
- 1% incontinence compared to over 25% risk with whole gland prostatectomy
Early detection saves lives. Let’s start with yours.
Ask for your Patient Navigator at your center offering Halo Pathways.
We are focusing on early detection for diseases causing approximately
half of deaths in the US every year.⁷

Cardiovascular Disease
Early detection of cardiovascular disease leads to better outcomes, fewer emergencies, and a longer, healthier life.

Dementia
Early detection of dementia empowers patients and families to take action – supporting better outcomes, improved quality of life, and more time to prepare for what’s ahead.
References
¹ Breastcancer.org; ² AhaJournals.org; ³ cancer.org; ⁴ American Cancer Society. Cancer Prevention & Early Detection Facts & Figures Tables and Figures 2024. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2024; ⁵ National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, and Pancreatic (Version 3.2025). NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Available at: https://www.nccn.org; ⁶; ⁷ Centers for Disease Control;